ENGENDERING EDUCATION
A Breakthrough Magazine
![]()
Empower. Educate. Transform.
COPYRIGHT
Engendering Education
Issue No.5
Editor-in-Chief:
Nayana Chowdhary
Commissioning Editor:
Urvashi Sarkar
Editorial Team
Barsha Chakraborty
Epti Pattnaik
Saswati Chatterjee
Design & Illustrations:
Aditi Dash
Website Design:
Shioft Digital Service Pvt Ltd
Sonalika Goswami
Published by Breakthrough Trust, New Delhi, 2025.
Breakthrough Trust,
Plot-3, DDA Community Centre, Zamrudpur,
New Delhi, Delhi 110048
![]() contact@inbreakthrough.org
contact@inbreakthrough.org![]() inbreakthrough.org
inbreakthrough.org
Download this publication for free at: engenderingeducation.in
Write to us at:
editorialteam@inbreakthrough.org
This publication is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike 4.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0). To view a copy of this license, visit: www.creativecommons.org/licences/by-nc-sa/4.0/.
All photographs used with permission from the contributors and their respective organisations.

Contents
| Nayana Chowdhury | THE LEDE |
From Access to Impact
| Annette Francis and Torral Parmar | COVER STORY |
Education
| Rumani Ahuja | CHANGE MAKER |

Editor’s
Note
Nayana Chowdhury
Innovation is unfolding rapidly with recent giant advances in technology, especially the growth of AI which is significantly affecting all areas of human activity. Education too has not been left untouched. Like other fields, education has also benefited from the progress in technology, though on the downside, its technological applications is seen as a lucrative market by service providers and technology entrepreneurs.
The intersection of technology and education is not new or recent. The 1920s saw the exciting new technology at the time, the radio1, being explored as a way for educators and university professors to disseminate educational lectures right into people’s homes. While not exactly a ‘digital classroom’ as those seen today, this is a prime example of technology being used as a way to improve accessibility and reach a sizable number of students.
Technology has interacted with education at various levels from the arrival of overhead projectors in schools to the use of handheld calculators (if frowned upon by some maths teachers). Personal computers for education purposes began being used in schools in the United States by the 1980s. By the early to mid-2000s, computers or ‘computer labs’ in schools in different parts of the world became ubiquitous.
The use of technology in education grew at a steady pace through the early 2000s and beyond. With expanding internet penetration in vast geographies of the country, the possibilities and potential for education to reach different constituencies of learners became immense. It was during the COVID-19 pandemic that technology enabled education became a dire necessity and hence all encompassing, but also at the same time the cracks started becoming visible.
The ‘digital classroom’ evolved from interactive screens or tablets being used in physical classrooms, to a space of its own: conducted through Zoom or Google Meet calls, with lessons or homework distributed through WhatsApp or with tuitions being conducted through YouTube videos. However, does it manage to deal with the challenges of access –whether due to availability or due to associated norms around digital access? Could everyone learn?How far does one need to go to reach the last mile learner in every household?
Accessibility issues seen in physical classrooms do not necessarily disappear when conducted online, or manifest in different ways. The gender, caste and class location of learners can have a bearing in online spaces too and perhaps more so when used in the confines of a home.
The mobile gender gap report 2025 also shows that there are 235 million women who are not using a smartphone compared to men². Even in cases where women own or use mobile phones, many have not yet adopted the use of mobile phone internet or simply own a handset without any mobile phone capability.

A myriad social norms affect the usage of phones in India, starting from the point of access. Even in cases of usage, many people face close surveillance. Although we often hear about the reach of the internet and digital devices, when one reaches the ground and tries to unpack the truth, a different picture presents itself. We have found that in many households where there is only a single mobile phone, it is given for use to the men of the household – fathers and sons – and therefore, many women often get forgotten or left out. This negatively impacts women’s education in an increasingly digitised world and they become the ‘last learners’.
The Close Up takes a look at the Kerala government’s KITE (Kerala Infrastructure and Technology for Education) initiative which focuses on digital literacy and inclusion. At the core of it is FOSS, a free and open source software that provides easy to access educational resources for teachers and students and helps with unrestricted sharing and revising.
And finally, the Changemaker for this issue is Rumani Ahuja, the teacher behind the popular YouTube channel ‘Magic of Maths by Rumani’. Using interactive assignments and visual aids through YouTube, Rumani attempts to instil a love of mathematics in her students and bust the fear and phobia around the subject.
Nayana Chowdhury
Editor-in-Chief, Engendering Education
SOURCES:
1https://daily.jstor.org/can-radio-really-educate/
2The Mobile Gender Gap Report 2025, GSMA (https://www.gsma.com/r/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/The-Mobile-Gender-Gap-Report-2025.pdf)
Kerala’s KITE
Flies High,
Shows the Way
for ICT Enabled
Education
KITE
In Kerala, an ICT revolution among school students has been underway since the early 2000s, courtesy a path-breaking initiative of the Kerala government which has digital literacy, inclusion, and a free and open source software (FOSS) model at its center. Anvar K. Sadath, CEO of KITE (Kerala Infrastructure and Technology for Education) speaks to Engendering Education about why this programme stands out and is being emulated in different parts of the world.

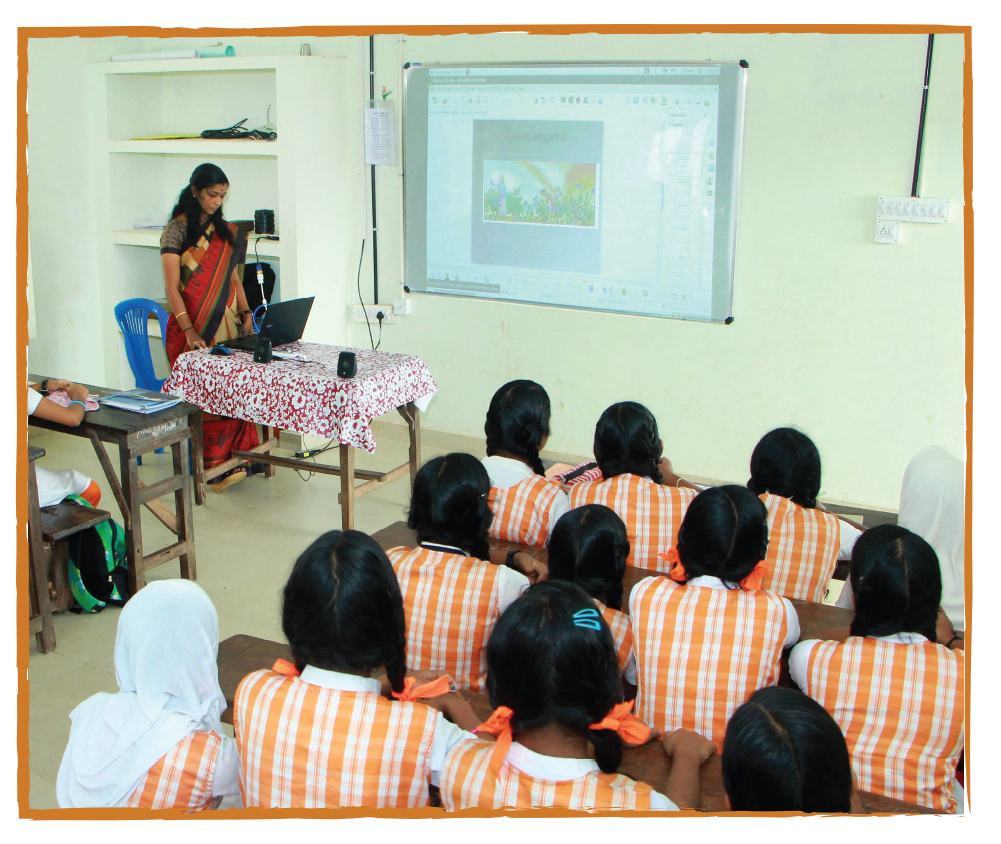
In the early 2000s, India’s IT revolution was yet to take off with computers still a novelty. Computer laboratories existed in some schools but students were not allowed a free hand with machines. This was the case for much of the country.
Schools in Kerala too had limited computers. But local school authorities and the state government were cognizant and had the foresight that children should have an early grasp over information and communication technology (ICT).
“There was no standardisation in machine specifications and no prescribed ICT syllabus. Teachers had little support or training to teach IT and questioned change,” said K. Anvar Sadath, CEO of KITE (Kerala Infrastructure and Technology for Education).
To assess the matter, a task force led by Prof. U.R. Rao in 2000 recommended creating a dedicated wing within Kerala’s education department to make interventions in information technology. This led to the establishing of ‘IT@School’ in 2001-2002, an initiative which systematically introduced ICT in schools in the state.
Under the project, information technology became a compulsory subject in Standard X and broadband connectivity was brought to schools. ICT based textbooks were taught in schools from Standard IX-XII. ICT infrastructure was brought to 4071 schools during 2007-2012 and students began to learn about animation, cyber safety, hardware, electronics and Malayalam computing from an early age.
The transition from IT@School
to KITE
IT@School was later renamed to Kerala Infrastructure and Information Technology for Education (KITE) in 2017 with its new status as a government company. The new status allowed KITE more scope and authority for implementing various ICT programmes. The broader aim was to foster digital technology literacy in government and aided schools, and competency among students.
Particularly during the COVID-19 lockdown, KITE ensured the broadcast of specially framed e-curricula to over 4.6 million students in the state.

Students absorb technology skills in a KITE classroom. Photo: kite.kerala.gov.in
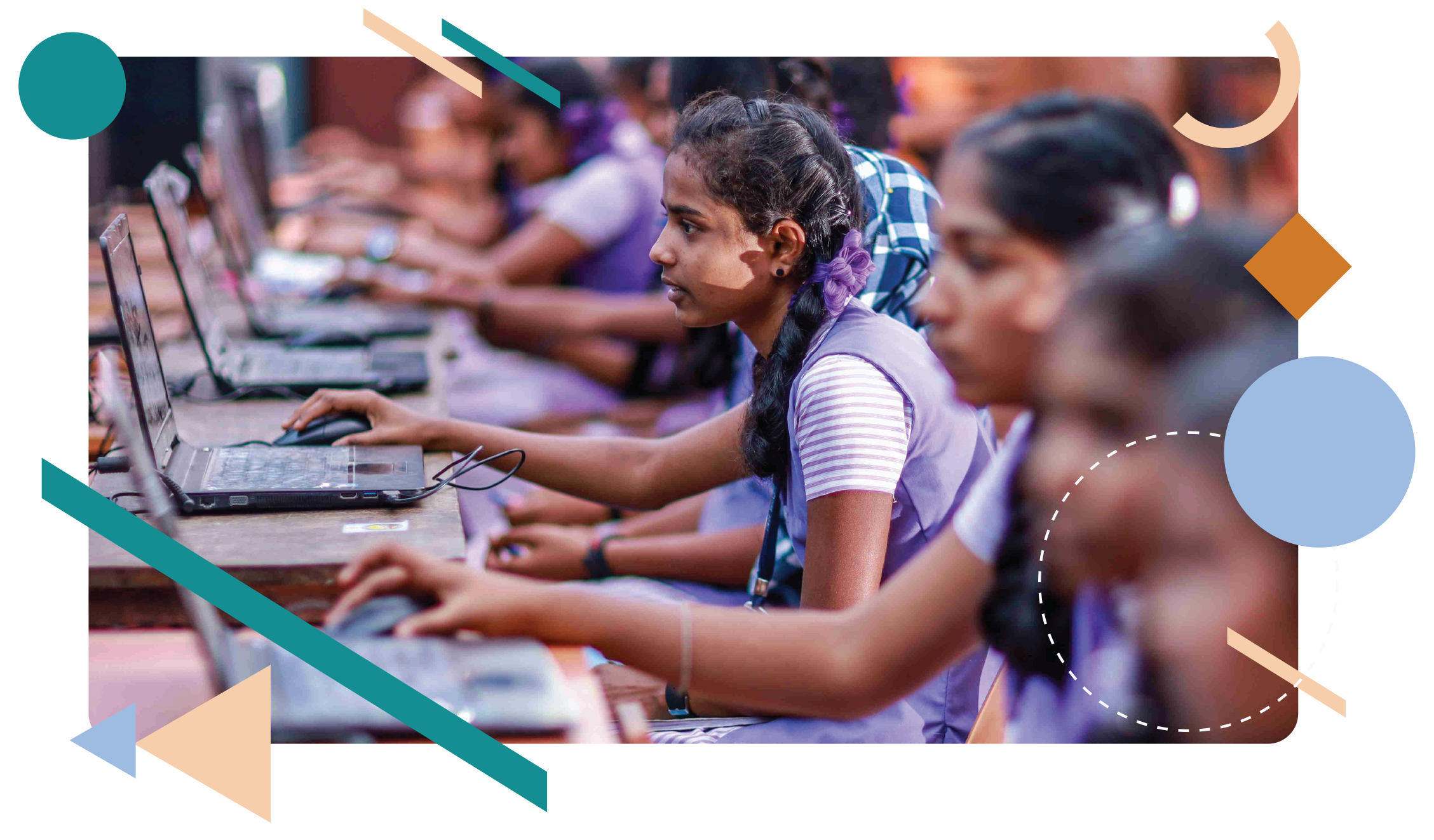


Girls have been equal beneficiaries of ICT-enabled education in Kerala’s schools. Photo: kite.kerala.gov.in
The flagship programme of KITE is the ‘Little KITES’ programme implemented in government and aided schools. Little KITES envisages that students not only use technologies but also contribute to the development of new software and tools and share their learnings with one another.
“Little KITES is the largest ICT student network in the country,” Sadath says. Over 1,80,000 high school students (Grades VIII, IX, and X) are currently members of Little KITES clubs formed in over 2,174 government and aided high schools in the state (roughly covering 50% of the state’s schools). Since its inception in the year 2018 more than 12,00,000 students have benefited from the programme.
The aim of KITES is to promote digital literacy, cyber literacy, and language computing. Students are introduced to advanced technologies such as Internet of Things, Al, robotics, 3D animation, multimedia, electronics, and mobile app development. It fosters community, collaboration, and peer learning among students.
What is the gender balance in
the KITES programme?
Girls are equally represented in Little KITES as boys. “Little KITES has been able to improve girls’
participation in STEM, thus breaking prejudice against gender/girls,” Sadath says.
For the academic session 2023-26, girls were 50.1 percent of 33,723 of a total batch strength of 67,318 students. The trend was consistent during 2021-24 and 2022-25.
The heart of Little KITES: Free and
Open Source Software
KITE ensures that all computers in government and aided schools run free software-based operating systems (FOSS) with open digital content and open educational resources. “Besides the fact that free software and educational resources incur no charges, it also helps unrestricted sharing and editing/revising of educational content among teachers and students,” Sadath said.
Thus expanding the programme to more schools does not require any expenditure on software or content since it is free and open source. The only costs are hardware and connectivity expenses. KITE schools have laptops that utilise entirely free software, replacing the previously licensed software. The state government’s decision to use FOSS in the General Education Department since 2008 itself gave Kerala an early start and has helped save about INR 3000 Crore annually in infrastructural costs. Choosing FOSS over proprietary software has technological, economic, social, and pedagogical benefits.
The management helming Little KITES is also cognizant of issues related to excessive exposure to technology and problems of unequal access among students to digital devices.
Sadath says, “We also have offline methods to involve students. Otherwise, the digital divide will kick in. To prevent the overuse of machines and smartphones by children, we focus a great deal on cyber safety protocol and cyber vulnerability. We do not insist on digital applications in schools which require the internet. Rather, students should be able to complete their activities without the internet.”
In 2022, the KITES programme received significant recognition when Finland asked the KITE team and Kerala government to establish student IT Clubs along the lines of the Little KITES IT Clubs in Kerala.
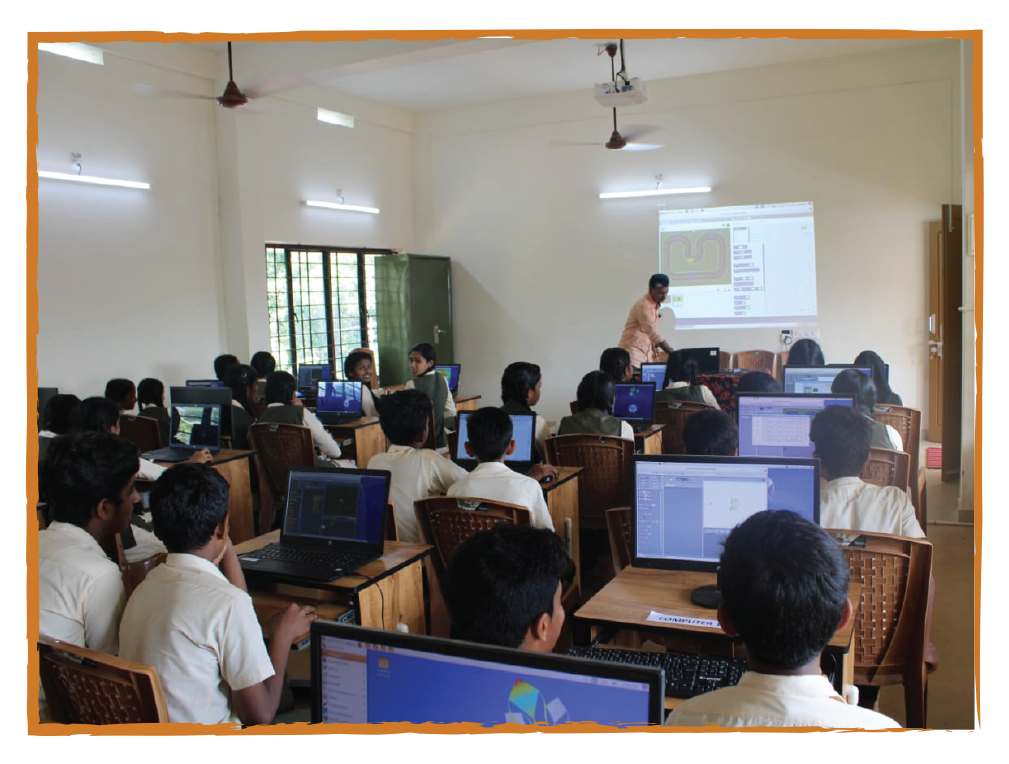

Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) is at the heart of the KITE programme. Photo: kite.kerala.gov.in
SOURCES:
1Soaring High. An Impact Study on Little KITES, Kerala’s Pioneering Digital Literacy Programme.
https://itforchange.net/sites/default/files/add/Soaring%20High%20-%20impact%20study%20on%20Little%20KITEs.pdf
2Empowering Adolescents with Future-ready Skills The inspiring story of `Little KITES’
https://www.unicef.org/india/media/10976/file/Empowering%20Adolescents%20with%20Future%20Ready%20Skills.pdf.pdf


Reimagining EdTech in India: From Access to Impact
Parmar (Pratham)
Annette Francis and Torral Parmar take a close look at the opportunities and pitfalls of the edtech sector. They provide a diagnosis of what is amiss, the gendered use of edtech, and what might be the way ahead.
How many hours did you find yourself engaging with the screen today? On an average1, people worldwide spend 6 hours and 42 minutes looking at screens. For children, this amount represents half of the total hours visible with screen time only increasing daily2. Screen content is actively re-shaping how we learn, think, feel, perceive and make choices every moment.
Technology is said to be ushering in a level-playing field, irrespective of geographical and cultural barriers. According to IBEF3, the Indian edtech market is currently valued at Rs. 64,875 crore (US$ 7.5 billion) and is expected to reach Rs. 2,50,850 crore (US$ 29 billion) by 2030. Many factors, including government interventions to promote digital tools for education such as DIKSHA, PM eVIDYA and SWAYAM, and innovative ed-tech companies have all contributed to the acceleration of digital learning in India. However, the COVID-19 pandemic was undoubtedly the catalyst needed to decisively cement the adoption of digital tools for learning. Edtech is no longer regarded as a peripheral experiment in education-it is at the forefront of defining the future of learning.
A growing digital infrastructure but a deep learning crisis
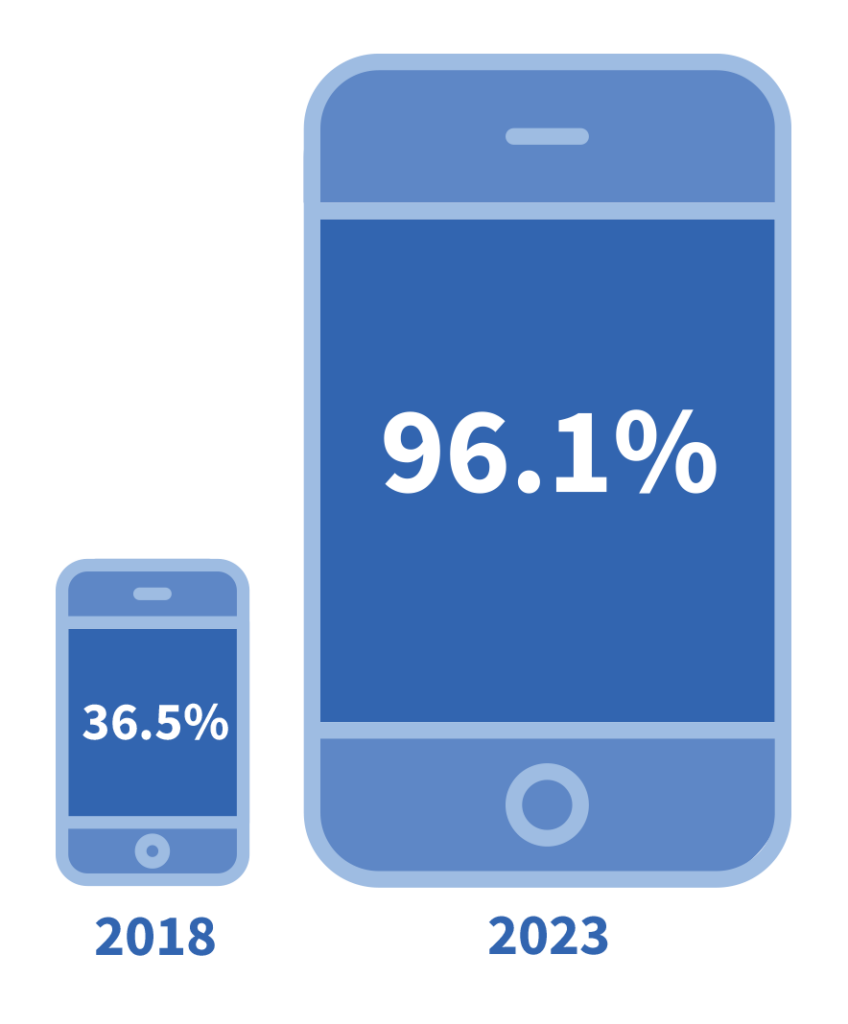
India’s digital access story is remarkable. In rural areas, smartphone penetration has surged from 36.5% in 2018 to 96.1% in 2023, according to ASER (Annual Status of Education Report). This has created an unprecedented opportunity to reach children and youth directly in their homes and communities. However, digital access alone is not translating into learning gains.

traditional setting, and which allows for tailored content and activities that gradually build mastery, will ensure no one is left behind due to a one-size-fits-all approach.
Dr. Wilima Wadhwa, Director of the ASER Centre, noted in the 2024 report: “The improvement trend is encouraging, but at the current pace, we would need another decade to ensure all children master basic skills.”
This disconnect highlights a core issue: technology must address the right problem. With smartphones in nearly every home, edtech should be laser-focused FLN gaps. But instead of building on existing usage patterns and adapting to learners’ real needs, many platforms continue to assume high levels of digital and academic readiness. This obviously leads to the exclusion of the most vulnerable.
Gendered usage and
unequal support
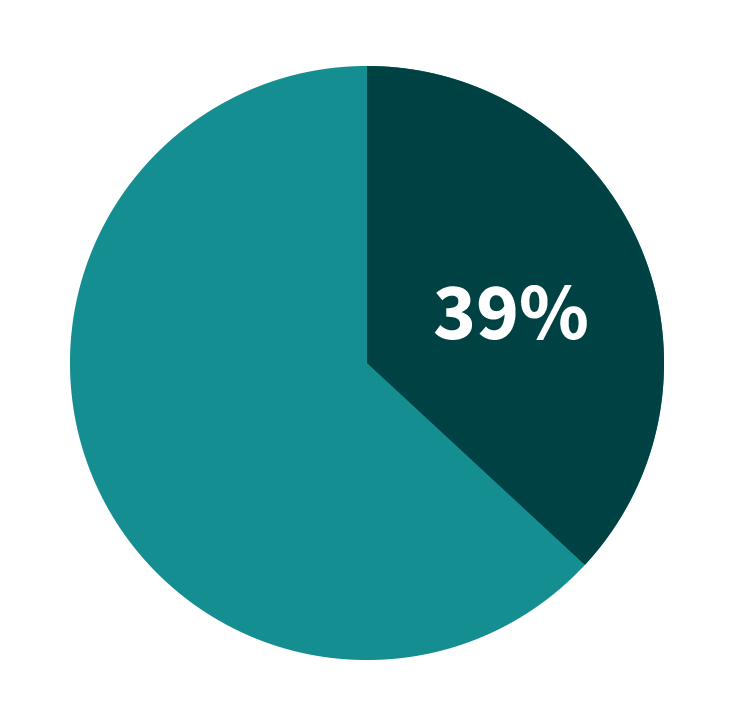
Early insights from ASER 2024 point to widening gender disparities in tech-based learning. While both girls and boys now have similar physical access to devices, only 27% of rural adolescent girls report independently using smartphones for learning-compared to 41% of boys. Girls also spend significantly less time on educational apps and face greater interruptions from household chores.
This gap is not just about device access-it is about social norms, family support, and motivation. Girls are 31% more likely to have their study time interrupted and 23% less likely to be encouraged to use tech for education. Without addressing these behavioral and structural barriers, edtech will continue to serve the digitally privileged, not the digitally excluded.
Recognising gaps: usability,
language, context, diversity
and trust
Rohit, 18, from rural Sitapur, UP, faced two barriers on a learning portal: he couldn’t navigate the login interface, and it requested personal information without context. The creators had made dual assumptions-users possessed both digital navigation skills and data literacy. For edtech to be effective, it must move beyond access and address usability. Many rural youth struggle to use digital platforms independently, and this challenge is even

Dr. Rukmani Banerji
CEO, Pratham Education Foundation
The contextualisation challenge is directly related to the existing FLN crisis. Most first-generation learners hesitate to interact with content when visuals, text, and voice-intonation are unfamiliar to them. Most ed-tech products fail to ground their content in familiar cultural, language and geographical contexts, presenting an added hindrance for the majority of children in India’s rural hinterland.
Trust in edtech is a significant yet uncharted barrier. ASER 2024 report states that 63% of parents from rural India expressed concern about data collection from educational apps, while 47% of surveyed adolescents reported abandoning educational platforms that required account creation or login credentials. As one parent from rural Bihar explained to ASER researchers: “I don’t understand what these apps are collecting about my child. Why do they need our family details? What if this information is misused?”
Designing for the last learner
India’s edtech ecosystem must fundamentally shift its focus-from merely engaging users to ensuring actual
Move from engagement to
meaningful learning
Simplify, localise, and humanise design
Designing for inclusivity involves several layers. Interfaces should be simple and not assume digital

fluency. Multilingual and non-text-based navigation should go beyond reading and writing, enabling understanding through visuals, voice, and interaction. Culturally relevant content should build trust and connection by anchoring learning in familiar contexts.
Build active and participatory
learning environments
Technology should not just deliver content-it should invite participation and co-construction of learning. Teachers can use smartphone apps for real-time polls, capture class sentiment, or collate and summarise student questions to drive responsive instruction. Interactive tools that help learners test, apply, and iterate on what they learn in real- world or simulated contexts.
Leverage the social layer of learning
Social media is the biggest competitor for learners’ attention and young people can experience adverse mental health and behavioral effects especially with
1https://backlinko.com/screen-time-statistics
2https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/india/42-children-below-age-of-12-spend-up-to-4-hours-daily-glued-to-screens-survey/articleshow/104147914.cms
3 https://www.ibef.org/news/india-s-edtech-market-likely-to-reach-rs-2-50-850-crore-us-29-billion-by-2030-report
4https://asercentre-org/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/ASER-2024-National-findings.pdf
5https://www.centralsquarefoundation.org/EdTech-Lab-Report-November-2019.pdf
6https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/indore/local-languages-to-be-medium-of-instruction-in-higher-edu-min/articleshow/121684315.cmst

Reimagining Mathematics Education
Rumani Ahuja
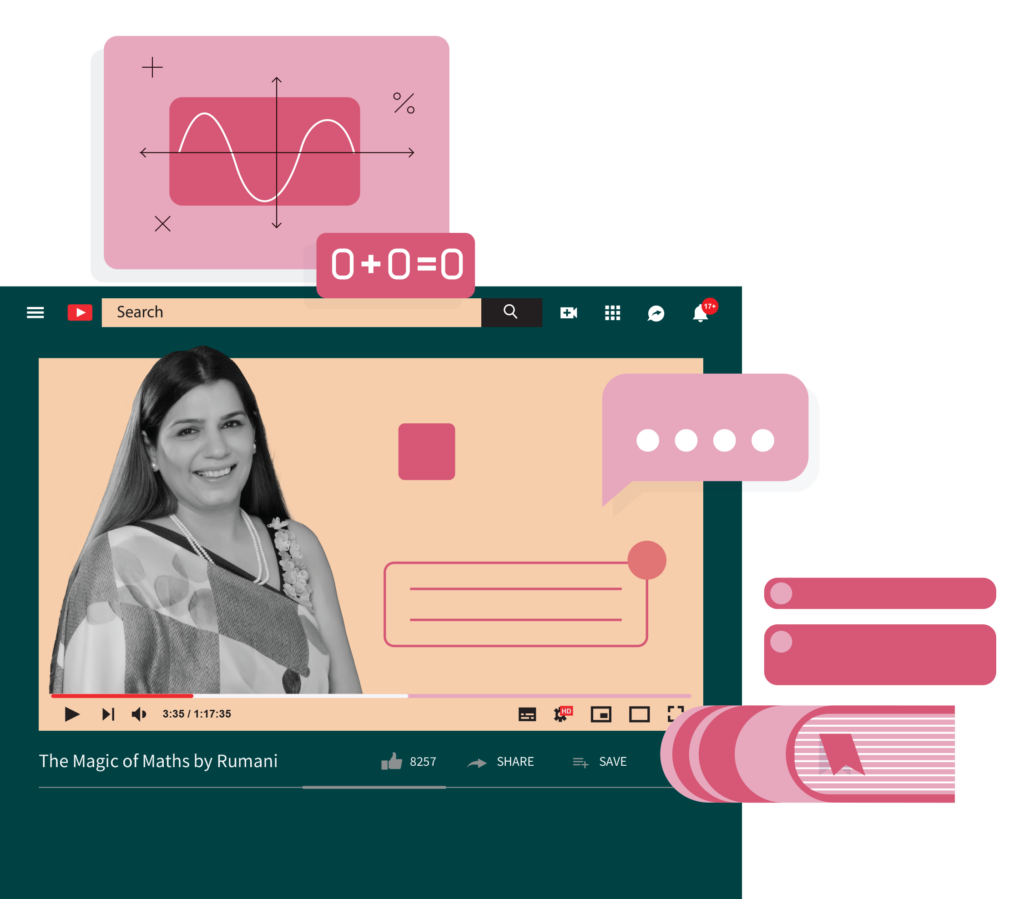

Rumani Ahuja’s YouTube channel ‘Magic
of Maths by Rumani’ is helping students
overcome their fears and apprehensions
around mathematics. With over 6000
subscribers and a steadily growing reach,
Rumani is helping students excel in
mathematics through interactive
assignments and visual aids. A teacher for
15 years now, Rumani is a dedicated
educator on a mission to bust fears and
phobias around mathematics. In a world
proliferated by YouTube male coaches and
experts, Rumani’s presence in the
online education sphere is making a difference.
What inspired you to pursue a career in education?
My journey in education commenced in 2010. I was influenced by my mother. I have always taught for the love of teaching. During the COVID-19 pandemic, I established “The Magic of Maths by Rumani” with the aim of inspiring students and making mathematical concepts more accessible.
Children have a phobia of maths and consider it as a tough subject. But it can become easy with the right methodology and correct techniques.
The integration of digital platforms into education has revolutionised learning. How have you utilized YouTube to enhance student engagement?
YouTube is a valuable educational resource. A simple share button facilitates the distribution of assignments and instructional content. I edit and caption my videos to ensure clarity. Through YouTube Shorts, I encourage students to showcase their own activities such as mathematical charts. This creates an environment where students feel motivated to participate and contribute.
You have an innovative approach to mathematics employing the use of visual aids. Could you elaborate?
Mathematics needs to be both interactive and tangible. I use origami (folding) and kirigami (cutting)
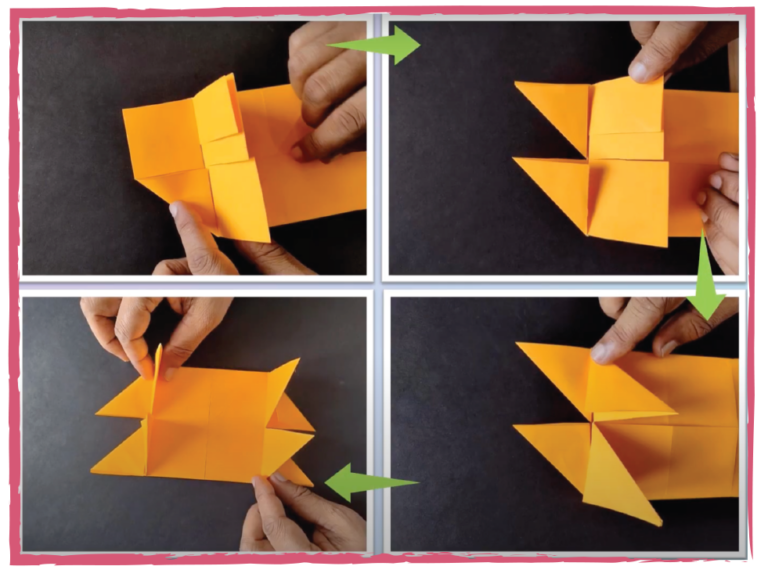
Image from Rumani's YouTube channel: https://www.youtube.com/@themagicofmathsbyrumani4143
to illustrate complex mathematical concepts. Whether demonstrating the Pythagoras theorem or geometric structures, these techniques are eco-friendly and reusable. My students have emulated these techniques and received awards on mathematical modelling and computational thinking. I have also designed an innovative activity book and file, targeting students from the sixth standard onward. These materials emphasize practical engagement and foster analytical thinking.
What initially drew you to mathematics, and how has your perspective on the subject evolved over time?
My appreciation for mathematics deepened through teaching. Mathematical learning is like the construction of a building-you cannot start from the seventh floor, a strong foundation is required first. Mathematics is a continuous process that extends beyond academia. My work in schools focuses on addressing students’ anxiety surrounding the subject, ensuring that they not only understand mathematics but also develop a genuine liking towards it.
In your opinion, do girls have a tougher time with mathematics?
Girls are responding well too. It is particularly gratifying to witness female students excelling in mathematics-one of my students is currently pursuing a PhD in the field.
How do platforms like Facebook and YouTube influence your pedagogical approach? Which has been your most shared content?
Digital platforms facilitate accessibility and allow students to engage with educational content irrespective of location. While students do not operate individual accounts, their parents assist in disseminating learning materials. One of my more ambitious projects, Geometricity, integrates quadrants, graphs, and three-dimensional geometric structures-such as cubes and prisms-to construct a city model that illustrates core mathematical principles. That caught on with a lot of students online.
Managing Professional
responsibilities alongside YouTube
content creation must
be a demanding task. How do you
balance your commitments?
I do not create content on a daily basis; rather, I prioritise making learning material that genuinely impart mathematical concepts in an interactive manner, through quizzes for example. The idea is to celebrate mathematics rather than employ it for commercial ends. I also teach in a government school and have to fulfill departmental duties. To ensure effective communication, I present content in both English and Hindi.
Does your work inspire fellow
educators? What do they want to
learn from you?
Teachers do inquire about my approach to increasing subscribers. I do not engage in content creation for commercial gain. My sole motivation is the advancement of student learning. I also conduct coaching classes, not with financial intent, but to foster mathematical understanding and
curiosity among students. My passion for teaching and learning knows no bounds and I am forever on a mission of making learning more engaging and joyful for my students.
You have been honored with
several prestigious awards. How
have these recognitions influenced
your journey?
In 2022, I was conferred the Malti Gyan Peeth Puruskar. Additionally, I was conferred the Punjab Teacher of the Year award in Amritsar. Other recognitions and laurels have come my way too. These accolades inspire me to contribute meaningfully to the field of education.
What advice would you offer to students who struggle with mathematics?
It is imperative to overcome the fear of
mathematics. Engaging students through interactive methods helps them develop an interest in mathematics and do better.
Image from Rumani's YouTube channel: https://www.youtube.com/@themagicofmathsbyrumani4143

Meet The
Contributors

Nayana Chowdhury
Nayana Chowdhury is the CEO of Breakthrough. With more than 25 years of experience in working in the social sector, Nayana vouches for the power of collective action in ensuring that it is the most marginalised who lead, both with their stories and in bringing together others in the community.

Annette Francis
Annette Francis is the Program Director for Vocational Training at Pratham Education Foundation, where she has been leading the organization’s youth skilling initiatives since 2018. Her work focuses on workforce development and technology-driven skill training, aiming to prepare India’s youth for the evolving demands of the job market.

Rumani Ahuja
An educator and teacher, Rumani helms the popular YouTube channel ‘Magic of Maths by Rumani’. Using interactive assignments and visual aids through YouTube, Rumani attempts to instil a love of mathematics in her students and bust the fear and phobia around the subject.

Torral Parmar
Torral Parmar is a Senior Manager, Research at Pratham’s youth training arm, where she leads research initiatives. Her key areas of interest include learning design and impact measurement within the vocational education, entrepreneurship, and livelihoods space.

KITE
Kerala Infrastructure and Technology for Education (KITE) is a Government of Kerala establishment set up to foster, promote and implement modernisation of educational institutions in the state of Kerala. At the core of it is FOSS, a free and open-source software that provides easy to access educational resources for teachers and students.